Table of Contents
What is a RAM Memory
WHAT IS RAM? Random-access memory (RAM) may be a series of tiny cards or modules obstructed into slots on the motherboard. The C.P.U. can request any information in RAM. It’s then situated, opened, and delivered to the C.P.U for processing in a few billionths of a second. Since all the contents of RAM are erased once you put off the pc, RAM is the temporary or volatile storage location for the PC.
 Figure: A RAM Memory Module.
Figure: A RAM Memory Module.
Operation:
Similar to a microchip, a chip is an integrated circuit (IC) product of a lot of transistors and capacitors. within the most typical variety of computer memory, dynamic random access memory (DRAM), a semiconductor unit and a capacitor are paired to form a memory cell, that represents a single little bit of information. The capacitor holds a little bit of info – a 0 or a 1. The transistor acts as a switch that lets the management circuitry on the memory chip scan the capacitor or amendment its state.
| HEAT SINKS, FANS | PC POWER SUPPLY | MOTHERBOARD |
| Graphics, Sound, and Network Card | What is Cache Memory |
A capacitor is sort of a little bucket that’s ready to store electrons. To store a 1 within the memory cell, the bucket is full of electrons. To store a 0, it’s emptied. the matter with the capacitor’s bucket is that it’s a leak. in a very matter of a number of milliseconds, a full bucket becomes empty. Therefore, for dynamic memory to figure, either the C.P.U. or the memory controller must return along and recharge all of the capacitors holding a 1 before they discharge. The capacitors must be energized every 15ms or so (hundreds of times per second) to maintain their charge. To do this, the memory controller reads the memory and then writes it right back. This refresh operation happens automatically and is however dynamic RAM got its name. Dynamic RAM must be dynamically fresh all of the time or it forgets what it’s holding. The downside of all of this refreshing compared to SRAM is that it takes time and slows down the memory.
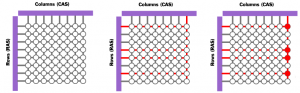 Figure: (a) Empty Memory Cells (a 0), (b) voltage applied to Column and Row lines (c) 4 cells charged
Figure: (a) Empty Memory Cells (a 0), (b) voltage applied to Column and Row lines (c) 4 cells charged
Memory cells are etched onto a silicon wafer in an array of columns (bit lines) and rows (word lines). The intersection of a bit line and a word line constitutes the address of the memory cell.
DRAM
DRAM works by causation a charge (an electrical signal known as a strobe) through the suitable column (CAS) to activate the transistor at every bit within the column. Once writing, the row lines contain the state the capacitor ought to take on. Once reading, the sense-amplifier determines the extent of charge within the capacitor. If it’s quite 50 %, it reads it as a 1; otherwise, it reads it as a 0. The counter tracks the refresh sequence supported that rows are accessed in what order. The length of time necessary to try all this can be thus short that it’s expressed in nanoseconds (billionths of a second). A chip rating of 70ns means it takes 70 nanoseconds to fully browse and recharge every cell.
Memory cells alone would be trifling while not a way to induce data in and out of them. That the memory cells have an entire support infrastructure of different specialized circuits. These circuits perform functions such as:
- Identifying every row and column (row address choose and column address select)
- Keeping track of the refresh sequence (counter)
- Reading and restoring the signal from a cell (sense amplifier)
- Telling a cell whether it should take a charge or not (write enable)
Other functions of the memory controller embrace a series of tasks that embrace distinctive the kind, speed and quantity of memory and check for errors.
- Once you open an application like Excel, it’s loaded into RAM. To conserve RAM usage, several applications load solely the essential elements of the program at first then load different pieces as required
- After an application is loaded, any files that are opened for use in that application are loaded into RAM.
- Once you save a file and shut the application, the file is written to the desired storage device, then it, and therefore the application is purged from RAM.
How Much RAM do you need?
The amount of RAM truly sitting on memory modules in your P.C is your computer’s physical memory. The memory that your software system uses is said as kernel memory. To see what proportion of RAM your P.C desires, check up on the memory needs for every program and add them up.
- You want RAM for the software system, application software system, and data. If your system responds slowly or accesses the disk drive perpetually, then you want to feature a lot of RAM
| Application | Minimum RAM Required |
| Windows 7 | 1000 MB |
| Microsoft Office Professional 2007 | 256 MB |
| Internet Explorer 8 | 128 MB |
| iTunes | 256 MB |
| Adobe Photoshop Elements | 512 MB |
| Total RAM required to run all programs simultaneously | 2,152 MB or 2.15 GB |
To save information a lot permanently, you want to avoid wasting it on the disk drive or on a different permanent device like a CD or flash drive.
Read-only memory (ROM) holds all the directions the P.C desires once it’s powered on. The information doesn’t get erased once the facility is turned off.
Metrics for RAM speed:
System RAM speed is controlled by bus width and bus speed. Bus width refers to the number of bits that will be sent to the C.P.U. at the same time, bus speed refers to the number of times a bunch of bits will be sent every second. A bus cycle happens whenever information travels from memory to the C.P.U. For example, a 100-MHz 32-bit bus is theoretically capable of sending 4 bytes of data to the CPU 100 million times per second, while a 66-MHz 16-bit bus can send 2 bytes of information 66 million times per second. If you do the sums, you’ll find that simply changing the bus width from 16 bits to 32 bits and therefore the speed from 66 MHz to 100 MHz in our example permits for 3 times the maximum amount of information (400 million bytes versus 132 million bytes) to undergo to the C.P.U unit each second for processing.
This post contains the content of book Computer Hardware_ Hardware Components and Internal PC Connection
